Introduction
The rise of automation and its effect on jobs has become a major concern in recent years. Automation, driven by technology and artificial intelligence (AI), has brought positive changes by making tasks easier, increasing productivity, and improving efficiency. However, it’s important to recognize the negative impact of automation on employment. This article aims to analyze the factors contributing to this negative impact, highlighting the tradeoffs and challenges involved.
Job Displacement and Unemployment
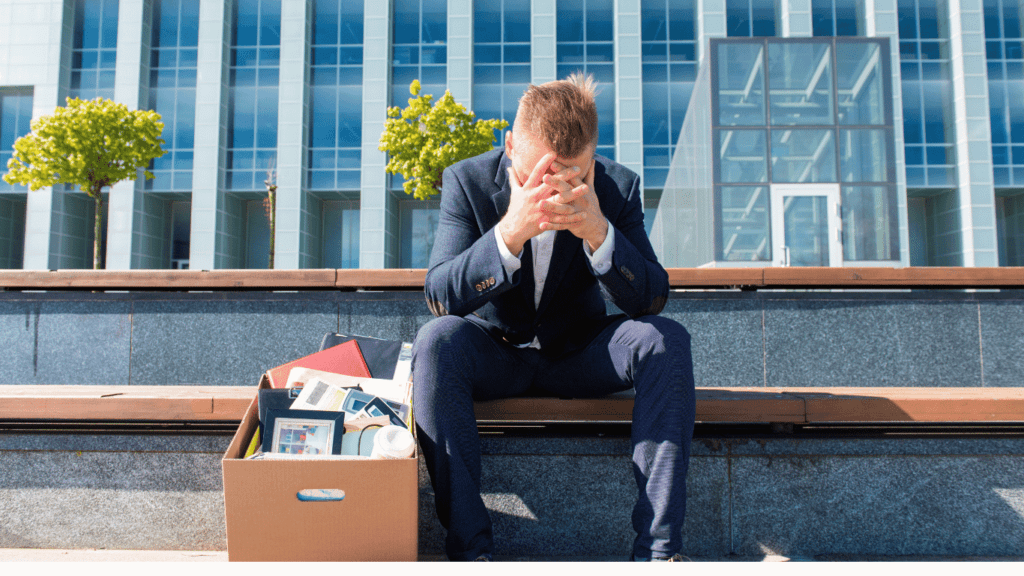

Automation can lead to job loss and unemployment as machines take over tasks previously done by humans. This affects sectors like manufacturing, transportation, retail, and even knowledge-based professions. For example, self-driving vehicles threaten professional drivers’ jobs, and robots in factories reduce the need for manual labor.
The challenge lies in retraining and finding new jobs for those whose jobs have been automated. While some argue that new jobs will emerge, the transition period can be difficult for individuals and communities relying on industries at risk of automation.
Growing Income Inequality
Automation can worsen income inequality by creating a gap between workers with specialized skills and those without. As technology advances, the demand for specialized skills increases, leading to higher wages for skilled workers. Jobs requiring lower skills and easily automated are at a higher risk of being replaced. This concentration of wealth can lead to socio-economic disparities and marginalization of lower-income communities.
Additionally, marginalized communities with limited access to education and training may struggle to adapt to an automated job market. Addressing the negative impact of automation on these communities is crucial.
Erosion of Job Quality and Security
Automation can lead to lower job quality and security. Although new jobs may be created, they tend to be more precarious and lower-paying than the ones they replace. This shift increases job insecurity and reduces stability, as workers face the constant threat of being replaced by machines. Job insecurity can have long-lasting effects on mental well-being and social cohesion.
Reduced Human Interaction and Service Sector
Automation not only affects traditional industries but also service-oriented sectors. Customer service, for instance, has seen significant automation with chatbots replacing human interaction. While this increases efficiency and reduces costs for businesses, it diminishes the human touch and empathy. The decline of service-oriented jobs affects individuals relying on such jobs for their livelihoods.
Implications for Education and Skill Development
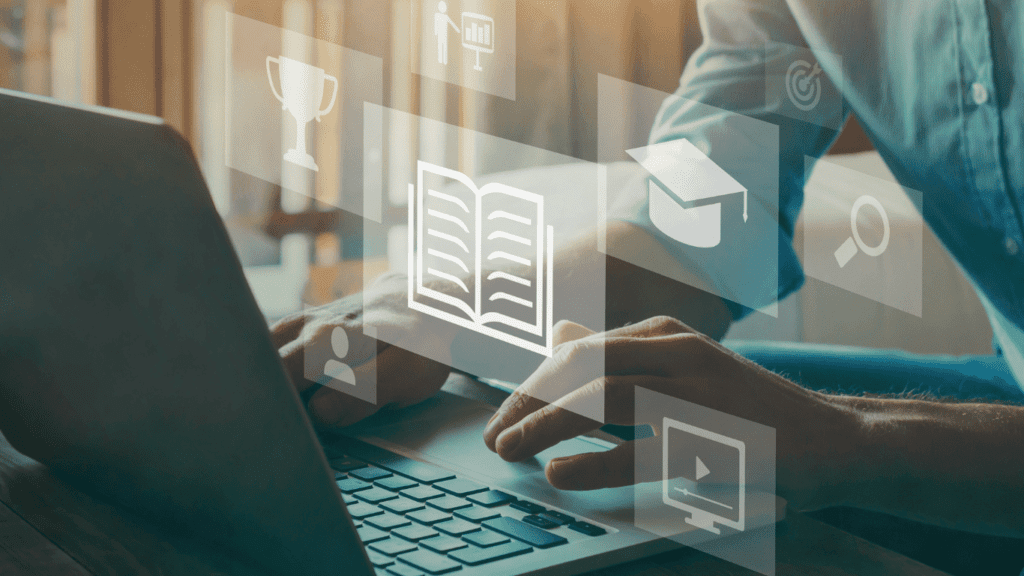

The negative impact of automation emphasizes the need for a shift in education and skill development. As automation takes over routine tasks, there is a growing demand for skills that complement automated systems, such as programming, data analysis, critical thinking, creativity, and emotional intelligence. However, ensuring access to relevant education and training is challenging, particularly for marginalized communities and those in lower-income brackets. Failing to address this issue could increase job market inequality.
Economic Disruptions and Structural Changes
Automation not only displaces individual jobs but can also cause significant economic disruptions and structural changes in local economies and communities. Industries and regions heavily reliant on jobs susceptible to automation may face severe challenges. For example, the closure of manufacturing plants due to automation can devastate entire communities. Governments and policy makers need to implement policies that support affected industries and facilitate the transition to new economic activities.
Ethical Considerations and Societal Implications
Automation raises ethical considerations and societal implications. Questions arise regarding fairness, equity, and the future of work as machines take over more tasks. It’s crucial to address issues like job displacement, income inequality, and the potential loss of purpose and identity for individuals affected by automation. Ethical frameworks should guide the development and implementation of automation technologies to align with soci values and promote human well-being.
Future Outlook and Mitigation Strategies
Looking ahead, preparing for the future of automation and employment is crucial. Predictions suggest automation will continue to impact various industries, necessitating proactive measures. Mitigation strategies include retraining and upskilling programs to equiptb individuals with the skills needed in the automated job market. Adopting a balanced approach to automation, considering social and economic consequences, can help mitigate the negative impact on employment.
Conclusion
The negative impact of automation on employment is a complex issue requiring careful consideration. While automation brings benefits, it also poses challenges like job displacement, income inequality, erosion of job quality and security, reduced human interaction, implications for education, economic disruptions, and ethical concerns. Policymakers, businesses, and society as a whole must address these challenges proactively and find innovative solutions for a fair and inclusive future of work. Continued research, dialogue, and collaboration are essential to navigate the complexities of automation and employment and shape a future that works for everyone.




One Response
Thank you for the auspicious writeup It in fact was a amusement account it Look advanced to far added agreeable from you However how can we communicate